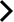Jinsha site was unearthed in February 2001 in Chengdu in an area spreading across about 5 square kilometers. It was the capital of the ancient Shu state, the center of the ancient civilization in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River from the 12th century BC to the 7th century BC. The excavation of Jinsha site marks the first major archaeological discovery in China since its first step into the 21st century, and it also reveals the existence of another historical relic in Sichuan Province following the famous Sanxingdui, wining itself the title of "Top Ten Archaeological Discoveries of 2001".

(Photo by MIK)
In April 2007, a museum carrying the three-thousand-year history of Chengdu soared skyward from where the site is. Covering the remains of Jinsha site, the museum serves to protect, research, and display the Jinsha culture and ancient Shu civilization. The Museum sits on a land of 300,000 square meters, and contains the Relics Hall, Exhibition Hall, Tourists Center, Cultural Relic Protection and Restoration Center, Jinsha Theater, Park Area etc., totaling a construction area of 38,000 square meters.
Stepping into the Museum, tourists will see the focus on the original ecological protection of the excavation site, which throws them right back into the magnificent and breath-taking riverside sacrificial scenes of ancient Shu state 3000 years ago, and reveals the secrecy of the meticulous and complex archaeological excavation work since 2001 with a plenty of precious cultural relics unearthed.
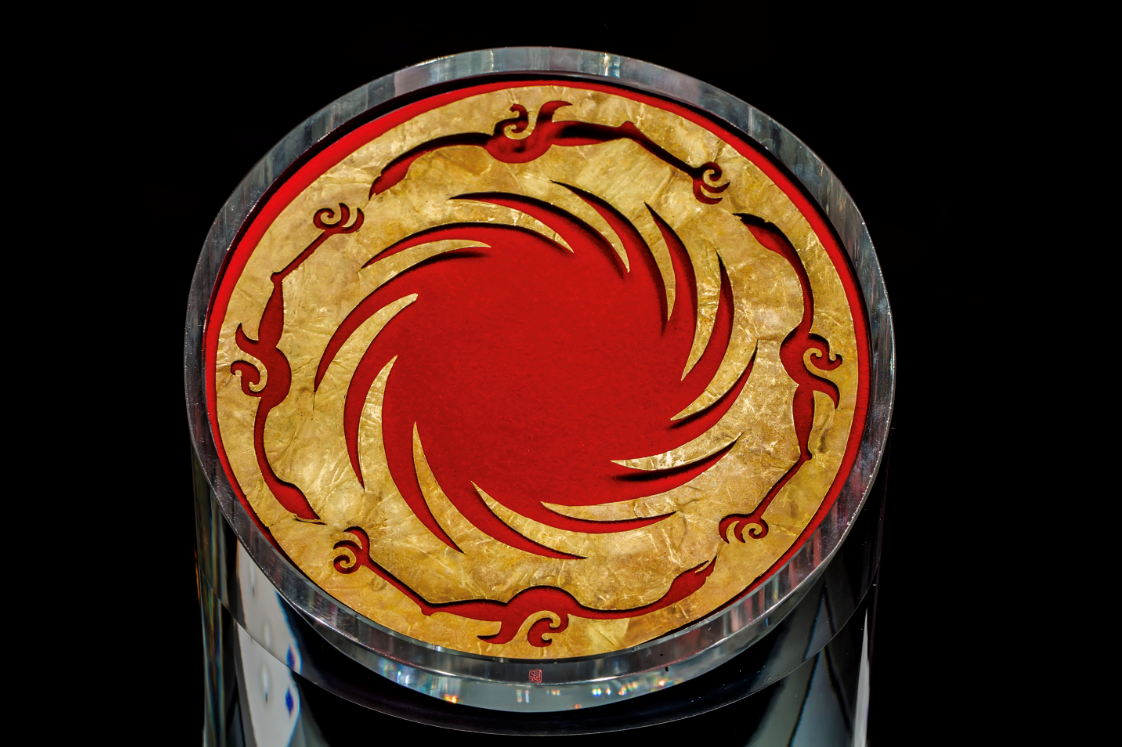

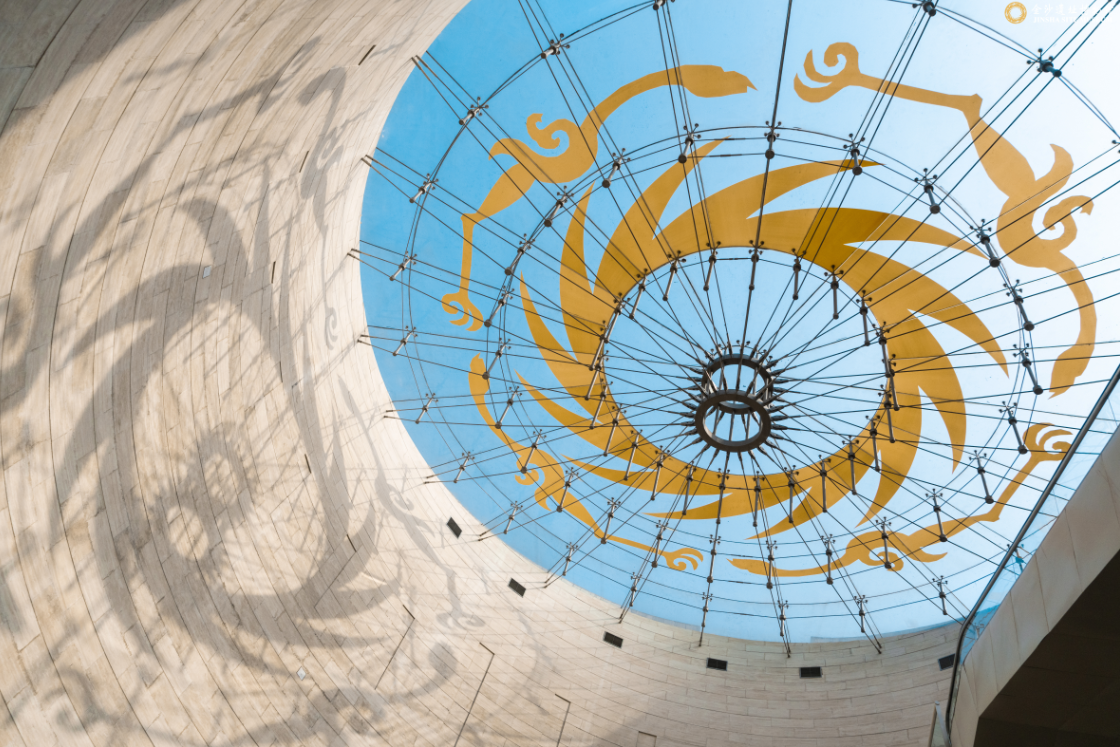
Sun and Immortal Birds Gold Ornament
(Photo by Jinsha Site Museum)
In December 2011, the Sun and Immortal Birds Gold Ornament unearthed at Jinsha site, the main design on China Cultural Heritage, was also confirmed as the core pattern of the urban image of Chengdu.
Today, Chengdu Jinsha Site Museum, the iconic landscape, not only tells widely the stories of Chengdu's long history and culture, but also has become an indispensable exhibition and research center for ancient Shu culture and a youth social education base.